46+ Actin Myosin Diagram
The N-terminal region of the myosin heavy chain forms the globular motor domain MD gray which contains the actin and ATP binding sites. Labeled are the key features of the molecule the ATP and actin binding sites the cleft between them and the a-helical region to which the myosin light chains.

Pin On Microbiology Notes
Troponin consists of three globular subunits.
. Web Single molecule of actin. Web How to draw a Diagram of Actin and Myosin in exam is the topic. The essential light chain ELC blue and the regulatory light chain RLC orange.
Residues 335-372 in an actin monomer of the. A higher level of excitation in RhoA generates a localized actomyosin peak with high contractility. The dark Z lines are a clear reference point in comparing this.
Where myosin head attaches during contraction. - Can be blocked. The process of cross-bridge cycling is shown in Figure PageIndex6.
Web A High resolution ribbon diagram of chicken S-1 myosin determined using X-ray crystallography. Away from the actomyosin peak RhoA. Web In this chapter we will characterize the structural and biochemical basis of the actin-myosin interaction and explain its relationship with myosins cellular roles with emphasis on the structural variation among myosin isoforms that enables their functional specialization.
In muscle actin molecules twist together to form a thin filament which interdigitate with thick filament bundles of myosin muscle protein. Web Skeletal muscle myosin dimers 40 nM are added to fully assembled F-actin networks and polymerize into thick filaments within the network 46 Fig. Cytoplasmic streaming facilitates the distribution of molecules and vesicles throughout.
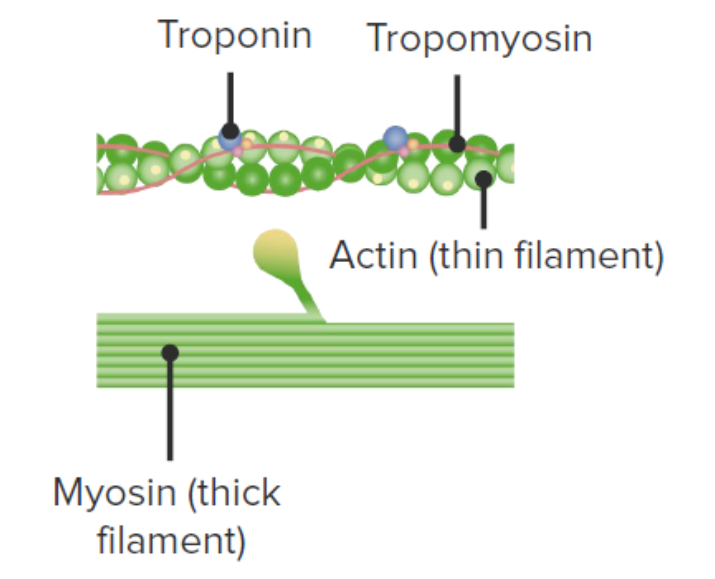
Web In muscles projections on the myosin filaments the so-called myosin heads or cross-bridges interact with the nearby actin filaments and in a mechanism powered by ATP-hydrolysis they move the actin filaments past them in a kind of cyclic rowing action. Web Myosin XI produces an intracellular flow known as cytoplasmic streaming in plant cells by moving on actin filaments while binding organelles via its tail domain. Web Actin has binding sites for myosin attachment.
Web Actin-myosin interactions play crucial roles in the generation of cellular force and movement. This is the well labelled diagram of structure of Actin Filament And Myosin Monomer. Actin-myosin interactions play crucial roles in the generation of cellular force and movement.
As can be observed actin binding is mediated by residues in the upper and lower subdomain cleft. Regulatory protein that binds to actin tropomyosin and calcium. The different classes of myosin motors provide for a number of types of.
Myosin via its cyclic interactions with actin filaments is a superfamily of molecular motor proteins that powers movement on actin filaments in all eukaryotic cells. One subunit binds to tropomyosin one subunit binds. In contrast myosin is a protein that produces dense contractile filaments within muscle cells.
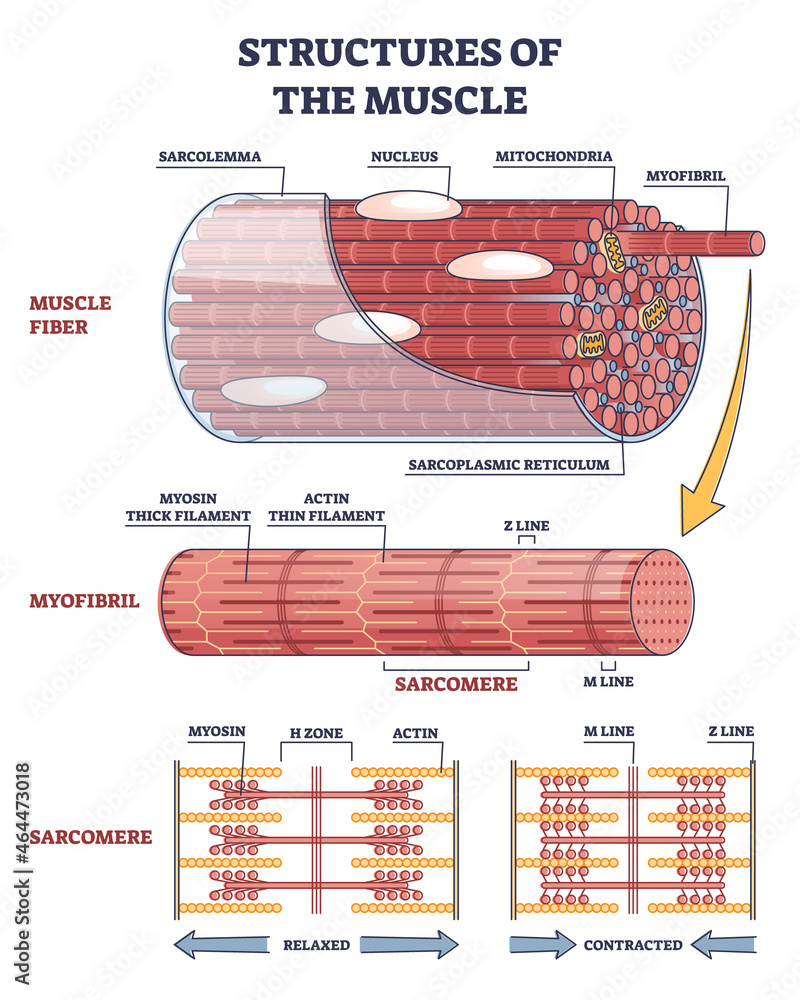
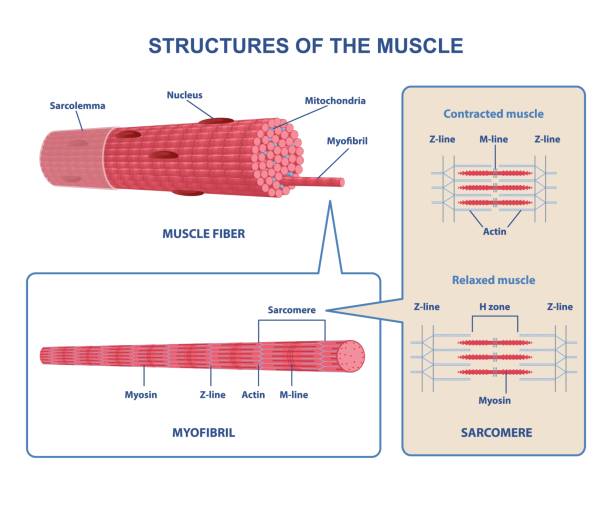
Human skeletal muscle is organized into sarcomeres. Web a Diagram of a class II myosin molecule. Web The myosin heads act on the actin filaments blue pulling them towards each other in a contractile movement.
The molecular mechanism involves structural transitions at the interface between actin and myosins catalytic domain and within myosins light chain domain. Myosin - Actin Interaction. Lets learn about the differences between.
2a b Supplementary Movie 34. The interaction of a myosin II S1 subfragment with an actin filament has been modeled. The molecular mechanism involves structural transitions at the interface between actin and myosins catalytic domain and within myosins light chain.
Web The main difference between actin and myosin is that actin is a protein that produces thin contractile filaments within muscle cells. This is a well labelled diagram of. Web 22 Myosin Design.
Strands of tropomyosin block the binding sites and prevent actinmyosin interactions when the muscles are at rest. A cross-bridge cycle begins when the. Web At higher S and moderate we observe propagating waves and pulsatile flows Fig 2C bottom.
Web The thin actin filaments also have binding sites for the myosin headsa cross-bridge forms when a myosin head binds with an actin filament. Covers myosin binding sites on the actin molecules. Web Supporting muscle contractions as actin filaments slide alongside myosin filaments.
Web In this chapter we will characterize the structural and biochemical basis of the actin-myosin interaction and explain its relationship with myosins cellular roles with emphasis on the structural variation among myosin isoforms that enables their functional.
30 Actin Myosin Illustrations Royalty Free Vector Graphics Clip Art Istock

Diagram Of Actin Filament And Myosin Monomer Drawing I Band And A Band Biology Diagram Youtube
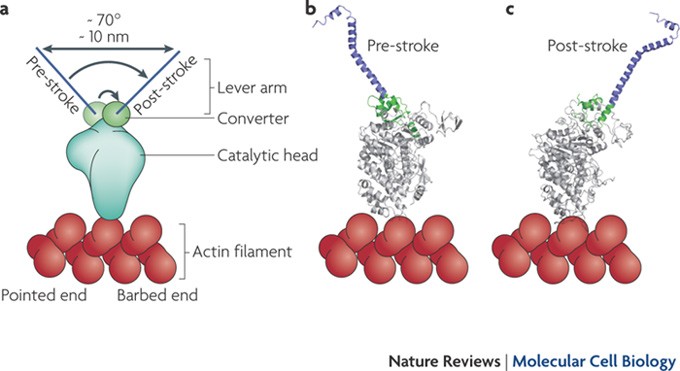
Myosin Vi An Innovative Motor That Challenged The Swinging Lever Arm Hypothesis Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

The Actin Myosin Cycle Modified From 6 Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic Illustration Of A Sarcomere Top With Actin Myosin And Download Scientific Diagram

Myosin Diagrams A The Classic Myosin Diagram Pictures Two Equivalent Download Scientific Diagram

Anatomy And Physiology Actin And Myosin Diagram Quizlet

How Myosin Generates Force On Actin Filaments Trends In Biochemical Sciences

File Sliding Filament Mechanism Diagram Pdf Wikipedia
Skeletal Muscle Contraction Concise Medical Knowledge
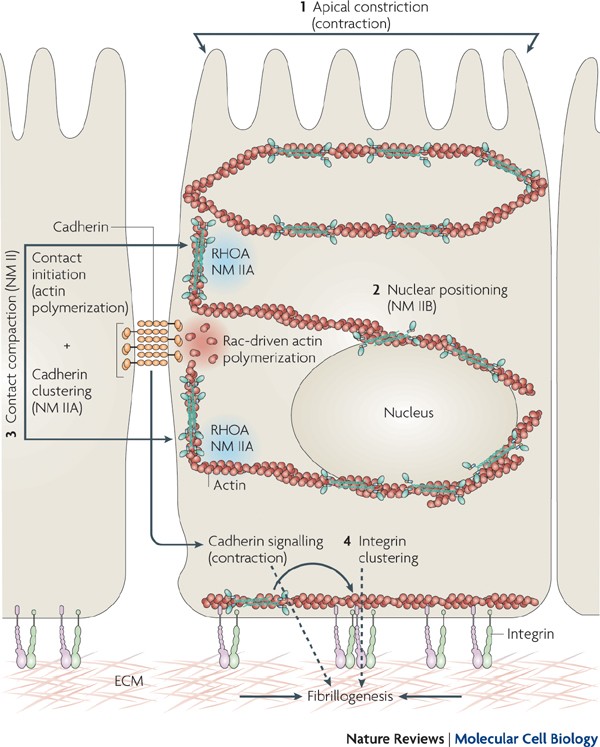
Non Muscle Myosin Ii Takes Centre Stage In Cell Adhesion And Migration Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

Explain The Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction With A Diagram

3 The Structure Of A Myofilament With The Actin And Myosin Filaments Download Scientific Diagram
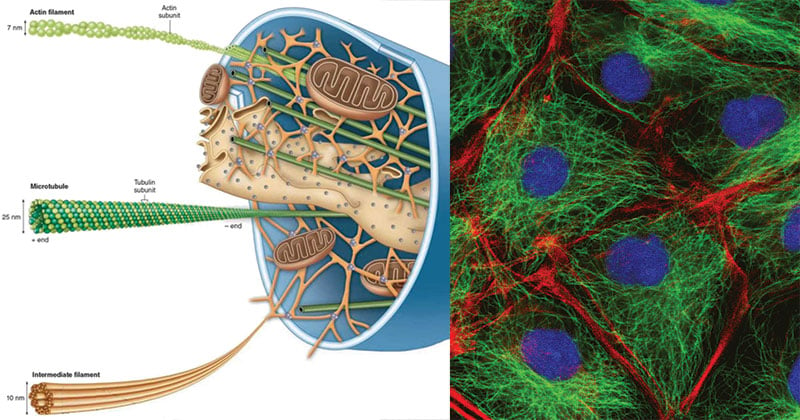
Cytoskeleton Definition Structure Functions And Diagram

Molecular Pumps And Motors Journal Of The American Chemical Society

Sliding Filament Theory Labster Theory
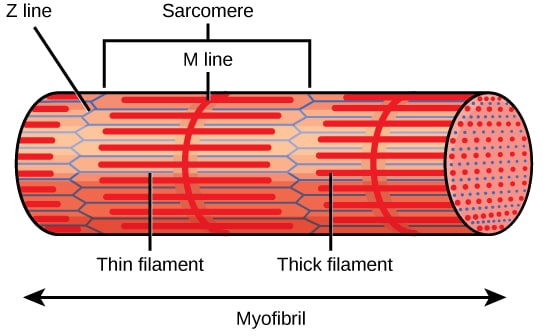
Skeletal Muscle Structure Contraction Teachmephysiology